Although parameters are at the very core of any BIM software, many users are confused about how to use it. But it’s very important to be familiar with parameters when you start modeling in a BIM software. Read about some useful tips on how to use parameters in Revit.
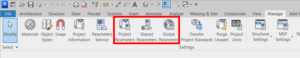
Revit provides four types of parameters: Project, Family, Shared, and Global parameters. For the first three types you need to decide do you want to use it for family types or for instances.
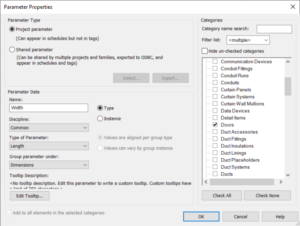
- Project parameters. The most commonly used parameters in Revit are project parameters. You have used them in every Revit project. Project parameters can not be used in external (loadable) families but it refers to external families loaded in the project and system families. You can use project parameters for scheduling but not in tags.
- Project Information. Project Information is a system family that you can access by navigating to Manage -> Project Information. It includes information that you mostly use for sheets and documenting. You can add new data to Project Information by using instance project or shared parameters.
- Transfer Project Standards. Project Parameters can be transferred between projects using “Transfer Project Standards” function. For more information see Revit tip #9.
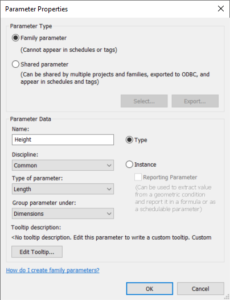
- Family parameters. The family parameters can be used only in family environment, so you can not use it in the project environment. Also you can not use family parameters in schedules and tags. Their primary purpose is to control the geometry and appearance of the families so the user can easily change family instances or create the new family types.
- Reporting Parameter. The family parameters provide an additional feature, and that is Reporting option. It can be used only if the parameter is for instances. With Reporting option checked you can report parameter’s value and use it in formulas and schedules.
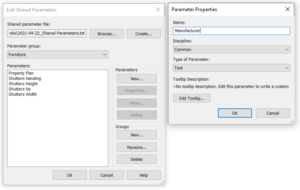
- Shared parameters. The shared parameters are the most powerful but also the most confusing parameters. You can use shared parameters in multiple projects and families which provides naming consistency and also allows you to match parameters from projects and external families. You need to specify the shared parameter file or create a new shared parameters file by specifying a simple TXT file that you created in Notepad. You should not edit this TXT file manually but only in Revit. Just go to Manage -> Shared Parameters. From here you can create new parameters in shared parameters file and group these parameters. Creating new parameters is very simple, you just need to specify name, discipline and type of parameter. Unlike project and family parameters, you can use shared parameters in tags (and also for scheduling) and in both project and family environment.
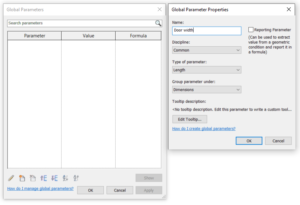
- Global parameters. The global parameters are usually the least used parameters in a Revit project. Global parameters control the values of other parameters globally. Global parameters can only be used in the project environment, in the single project file, and can not be used in schedules. Global parameters are not shareable. They are useful when you need to set up constraints, like corridor width, distance of doors from walls, etc. Without global parameters you should set constraints manually for every single case. Similar to family parameters, it also provides a Reporting option that you can use to report values and use it in formulas.